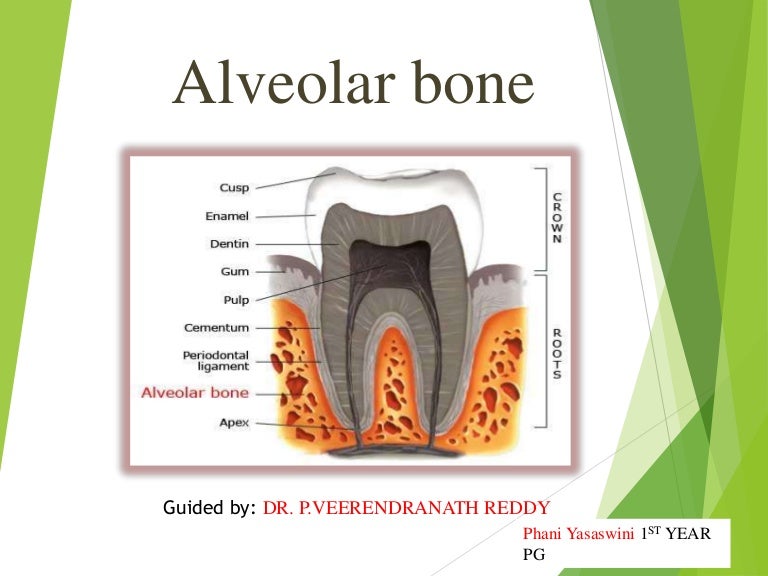
Alveolar Bone Biology Diagrams The alveolar process (/ æ l ˈ v iː ə l ər, ˌ æ l v i ˈ oʊ l ər, ˈ æ l v i ə l ər /) [1] is the portion of bone containing the tooth sockets on the jaw bones (in humans, the maxilla and the mandible).The alveolar process is covered by gums within the mouth, terminating roughly along the line of the mandibular canal.Partially comprising compact bone, it is penetrated by many small The alveolar crest is the most cervical rim found in the alveolar bone proper. When it is healthy, the alveolar crest is slightly apical to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) by about 1.5-2 mm. The alveolar crests of the adjacent teeth are also uniform in height along the jaw when they are healthy. The supporting alveolar bone structure consists The alveolar process (alveolar bone) is the thickened ridge of bone that contains the tooth sockets on bones that bear teeth (maxilla and mandible).On the maxilla, the alveolar process is a ridge on the inferior surface. It makes up the thickest part of the maxilla.The alveolar process contains a region of compact bone adjacent to the periodontal ligament called lamina dura. It is this part
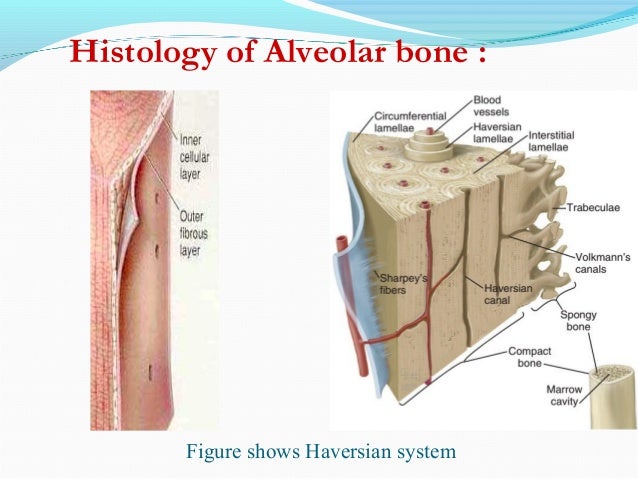
The alveolar bone is a dense bone that lines the tooth sockets, which are known as the alveoli, and is attached to the teeth by the periodontal ligament. Although the bone itself is dense and compact, it contains multiple small holes that allow blood and nerves to connect to the periodontal ligament and that house the fibers, called Sharpey The cortical bone, or cortical plates, consist of plates of compact bone located on the facial and lingual surfaces of the alveolar bone. These cortical plates are usually 1.5-3 mm thick over the posterior teeth. The thickness can drastically vary around the anterior teeth. The trabecular bone contains cancellous bone, which is between the

Periodontology Anatomy Biology Diagrams
Anatomically, alveolar bone is a quite complex tissue due to its functional demands. Before discussing various aspects of alveolar bone, first we need to go through the developmental aspect and the molecular aspect of bone formation. Cross section of mandible at first molar region showing cortical and spongy bone Basic concepts in osteogenesis Healthy bone density in your alveolar process is critical to support oral implants. To ensure that your alveolar process stays in top condition, it's important to avoid gum disease with a proper oral care routine. Advanced gum disease can cause lasting damage to your bone and disrupt its proper functioning.

Alveolar bone surgery includes alveolar osteoplasty, alveolar resection, and bone grafting, and it is often performed simultaneously with other periodontal surgical procedures. Alveolar bone reshaping is a surgical procedure that corrects alveolar bone morphology to a physiological form without removing the native alveolar bone.