BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION AT MOLECUL ES AND C ELL Biology Diagrams Key words: health effects; radiation damage; radiation protection; radiation, ionizing. INTRODUCTION. T he direct effect of ionizing radiation on the human body is typically manifested as a cytological effect, the worst of which is cell death. It is important to identify the mode of cell death caused by ionizing radiation and its molecular Multiple pathways are involved in maintaining the genetic integrity of a cell after its exposure to ionizing radiation. Although repair mechanisms such as homologous recombination and nonhomologous end-joining are important mammalian responses to double-strand DNA damage, cell cycle regulation is perhaps the most important determinant of ionizing radiation sensitivity. Cell cycle and cell proliferation following irradiation. Radiation-induced cell cycle changes were analyzed by flow cytometry at 0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42 and 48 h after X-irradiation using PI staining. The primary results are depicted in Fig. 3A. The change trend of S-phase under different doses of irradiation was similar, within the 24 h
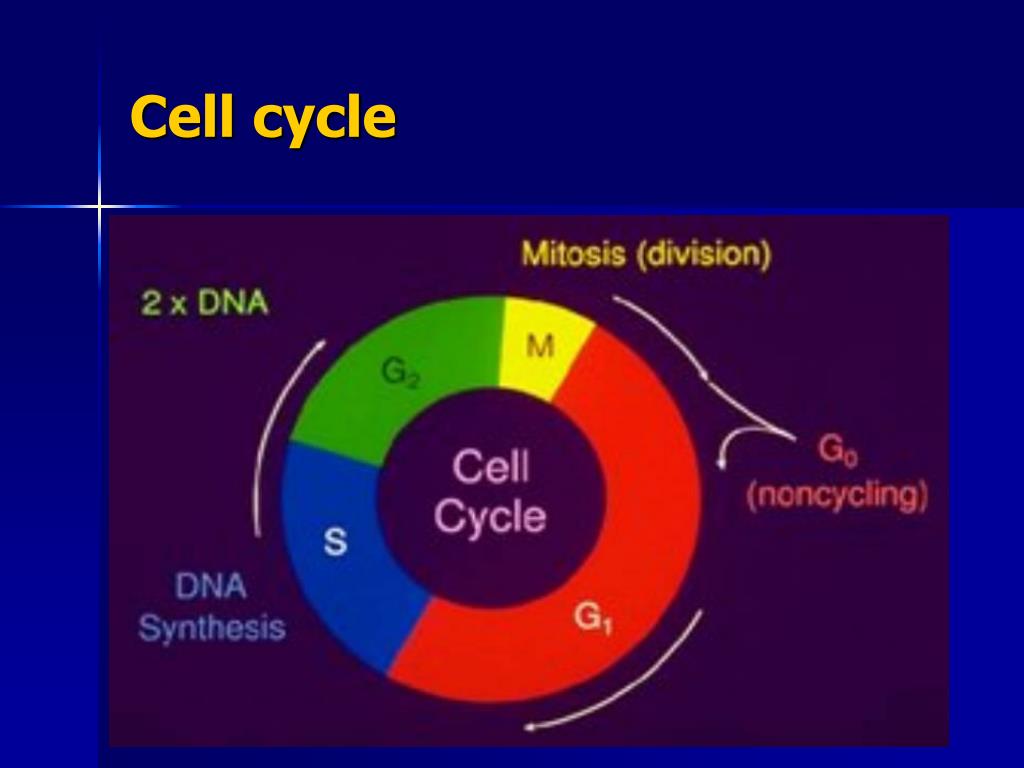
Irradiation of normal eukaryotic cells results in delayed progression through the G1, S, and G2 phases of the cell cycle. The G1 arrest is regulated by the p53 tumor suppressor gene product. Irradiation results in increased expression of p53, which in turn induces a 21 kDa protein, WAF 1/Cip 1, that inhibits cyclin CDK kinases. S-phase delay is observed after relatively high doses of radiation
Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy Biology Diagrams
Comparing isodoses, high-LET irradiation is a more potent inducer of cell cycle delays than low-LET irradiation. Generally, more pronounced delays in S- and G2-phase have been observed with increasing LET. The role of TP53 in relation to these effects is still controversial. A dose- and LET- depende … Cell cycle phase-dependent differences in radiosensitivity are considered important during clinical radiotherapy. One of the rationales described by the original four R's of fractionated radiotherapy is "Redistribution" of tumor cells into more radiosensitive cell cycle phases (Withers 1975b).If some tumor cells are in a radioresistant cell cycle phase at the time of the first fraction

Cell cycle progression can be studied with computational models that allow to describe and predict its perturbation by agents as ionizing radiation or drugs. Such models can then be integrated in The key proteins involved in cell cycle checkpoints in different phases of the cell cycle, and their interaction, is a fertile and rapidly developing area of research. This review summarizes the current state of knowledge of cellular checkpoints in response to radiation-induced double-strand breaks in mammalian cells and how this impacts on

ray irradiation on cell apoptosis, cell ... Biology Diagrams
Although understanding the concept of the cell-cycle phase is important to understanding ionizing radiation's effect on the cell, the therapeutic application of synchronization is extremely limited. Concerns about the therapeutic efficacy of synchronization therapy have come from a number of sources (199, 231-234). For example, Tubiana et al.
