Cytokines Principles and prospects Biology Diagrams Abstract. The primary goal of cytokinesis is to produce two daughter cells, each having a full set of chromosomes. To achieve this, cells assemble a dynamic structure between segregated sister chromatids called the contractile ring, which is made up of filamentous actin, myosin-II, and other regulatory proteins. This ring is also stabilized by anchor proteins FtsA and ZipA, which tether FtsZ to the inner face of the plasma membrane. Z-ring also acts as a dynamic scaffold to recruit downstream proteins with critical regulatory functions of cytokinesis, such as peptidoglycan (PG) remodeling and chromosome segregation (den Blaauwen et al. 2017). Thus, many levels of RhoA regulation appear to be at work and generally feed through Ect2, MgcRacGAP, and F-actin. Cytokinesis completion depends on ESCRTIII-mediated lipid dynamics. Membrane trafficking and remodeling play significant roles at the abscission stage during cytokinesis. ESCRT is responsible for membrane constriction and fission.

Among these proteins, FtsZ is recognized as a cytoskeleton protein because it can assemble into a ring-like structure called Z-ring at midcell. Regulation of cytokinesis: FtsZ and its accessory proteins Curr Genet. 2020 Feb;66(1):43-49. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-01005-6. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Authors Mingzhi Wang 1 , Chao Fang 1 , Bo Ma 1

Cell Division: Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Regulation Biology Diagrams
Mitosis and cytokinesis are key stages of cell division, each playing distinct roles in cellular replication. The regulation of these processes is tightly controlled by various molecular mechanisms. This article will explore the intricacies of mitosis, cytokinesis, and their regulation, highlighting the essential components and steps involved. Cytokinesis, the final step of cell division, is a great example of robust cell shape regulation. A wide variety of cells ranging from the unicellular Dictyostelium to human cells in tissues proceed through highly similar, stereotypical cell shape changes during cell division. Typically, cells first round up forming a cleavage furrow in the middle, which constricts resulting in the formation

In a typical cell, cytokinesis accompanies every mitosis, although some cells, such as Drosophila embryos (discussed later) and vertebrate osteoclasts (discussed in Chapter 22), undergo mitosis without cytokinesis and become multinucleate. myosin II filaments, and many structural and regulatory proteins. The primary goal of cytokinesis is to produce two daughter cells, each having a full set of chromosomes. To achieve this, cells assemble a dynamic structure between segregated sister chromatids called the contractile ring, which is made up of filamentous actin, myosin-II, and other regulatory proteins. Constriction of the actomyosin ring generates a cleavage furrow that divides the cytoplasm
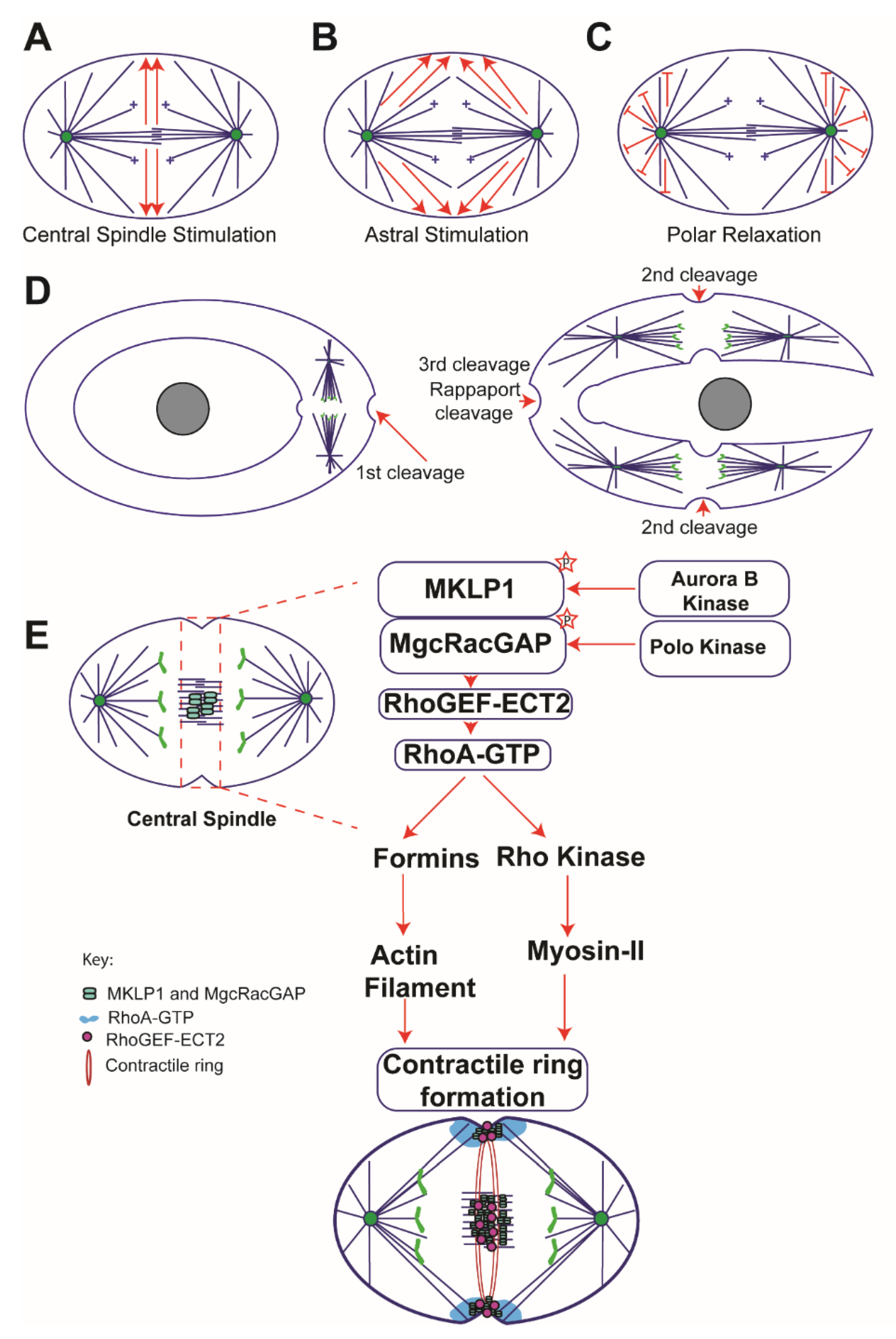
Regulation of cytokinesis: FtsZ and its accessory proteins Biology Diagrams
Second, endosomes may allow fast and localized delivery of regulatory proteins leading to the reorganization of the cytoskeleton and PM that is required for abscission to take place. In this mini-review we will not discuss the roles of specific lipids during cytokinesis, since several excellent reviews have been recently published on this topic
