Figure 1 from Dual Role of Heat Shock Proteins as Regulators of Biology Diagrams Here we show that the genome-wide transcriptional response to heat shock in mammals is rapid and dynamic and results in induction of several hundred and repression of several thousand genes.

Heat shock is a physiological and environmental stress that leads to the denaturation and inactivation of cellular proteins and is used in hyperthermia cancer therapy. Previously, we revealed that mild heat shock (42 °C) delays the mitotic progression by activating the spindle assembly checkpoint (S …

Heat Shock Factor HSFA6b Mediates Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein ... Biology Diagrams
Furthermore, the most famous transcription factor against temperature stress is heat shock transcription factor/heat shock factor (HSF). HSF was discovered as a transcription factor essential for the heat shock response. The heat shock response is a cellular protective mechanism against heat stress that was discovered by Ritossa in 1962. Background Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) is the master regulator of the heat shock response and supports malignant cell transformation. Recent work has shown that HSF1 can access the promoters of heat shock proteins (HSPs) and allow HSP expression during mitosis. It also acts as a mitotic regulator, controlling chromosome segregation. In this study, we investigated whether the transactivation
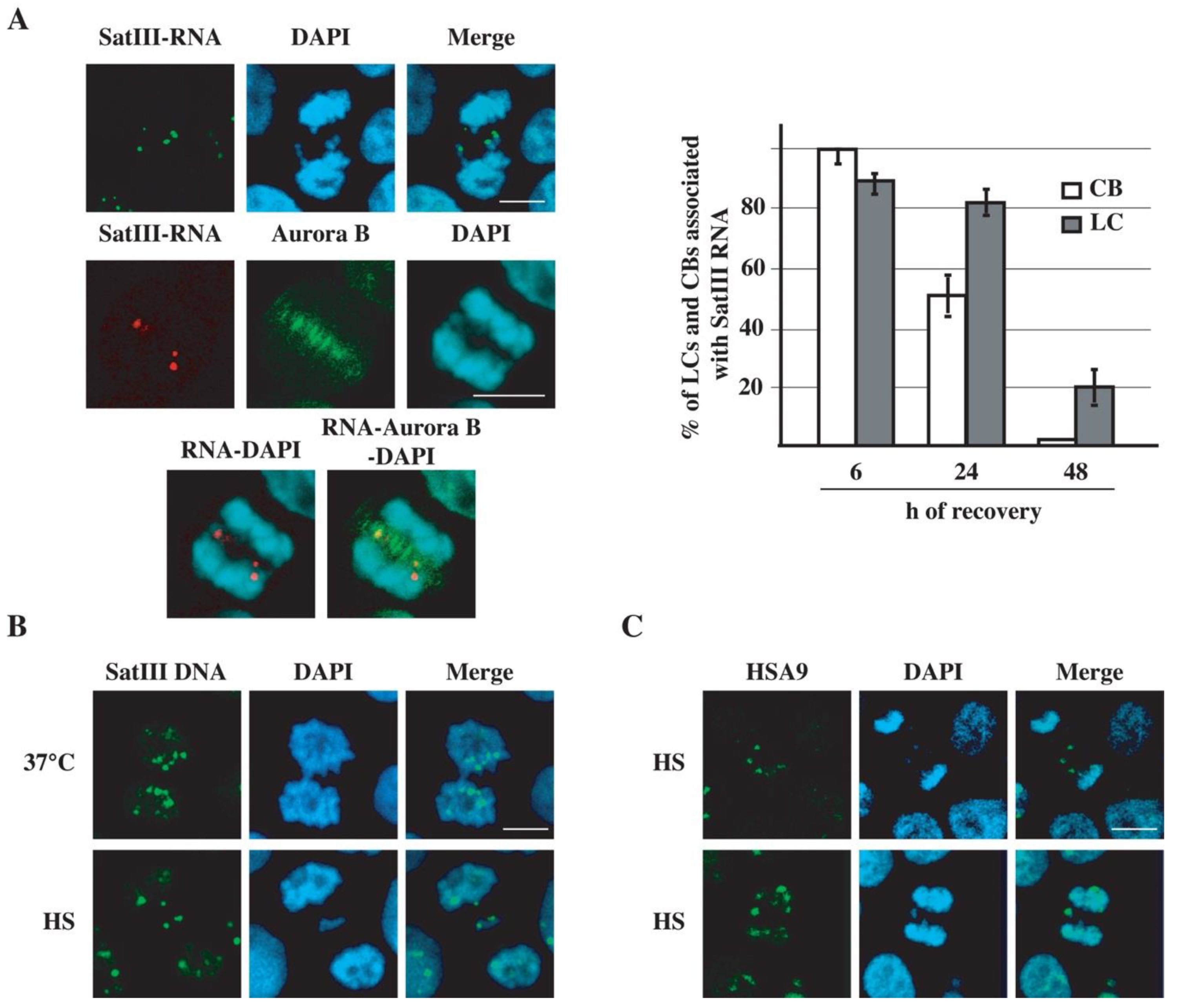
Heat shock causes proteotoxic stress that induces various cellular responses, including delayed mitotic progression and the generation of an aberrant number of chromosomes. In this study, heat shock

Heat shock transcription factors demonstrate a distinct mode of ... Biology Diagrams
This cytoplasmic protein stress response activates the transcription of heat shock protein (HSP) genes through the action of heat shock transcription factors (HSFs), which are crucial for preserving cellular protein homeostasis [19, 20]. During interphase, another transcription factor, HSF2, collaborates with HSF1 to switch on expression of heat-shock genes. During mitosis, however, cells become more susceptible to stress because they curtail this induction of heat-shock genes.
