Haploid vs Diploid cell and Cell division Biology Diagrams Diploid, Haploid Definition & Examples. Diploid (2n) = two copies of each chromosome. Haploid (n) = one copy of each chromosome. The haploid stage is less predominant than the diploid stage in the life cycle of most Pteridophyta like a fern. Type of eggs: Diploid organisms develop from fertilized eggs. In the diploid - dominant cycle, the multicellular diploid stage is the most obvious life stage; the only haploid cells produced by the organism are the gametes. Most fungi and algae employ a haploid-dominant life cycle type in which the "body" of the organism is haploid; specialized haploid cells from two individuals join to form a

Key Similarities Between Haploid and Diploid. Essential for Genetic Processes: Both haploid and diploid configurations are fundamental to the genetic operations within organisms, each playing distinct roles in growth, reproduction, and survival.; Integral to Life Cycle: Each configuration plays a critical role in the life cycles of organisms, particularly in the transitions between generations
Difference Between Diploid and Haploid Biology Diagrams
Main Difference - Diploid vs Haploid. Diploid and haploid are two terms which describe the number of chromosome sets present in the cell or the ploidy of a cell. In plants, fungi and algae, some stages of the life cycle are diploid, and some stages are haploid. This is referred to as the alterations of generations. In algae and fungi cells switch between a haploid and diploid state over the length of their life cycle "Diploid vs Haploid." Diffen.com. Diffen LLC, n.d. Web. 17 Mar 2025. < > Comments: Diploid vs Haploid. Anonymous comments (5) April 19, 2014, 10:35pm. super helpful

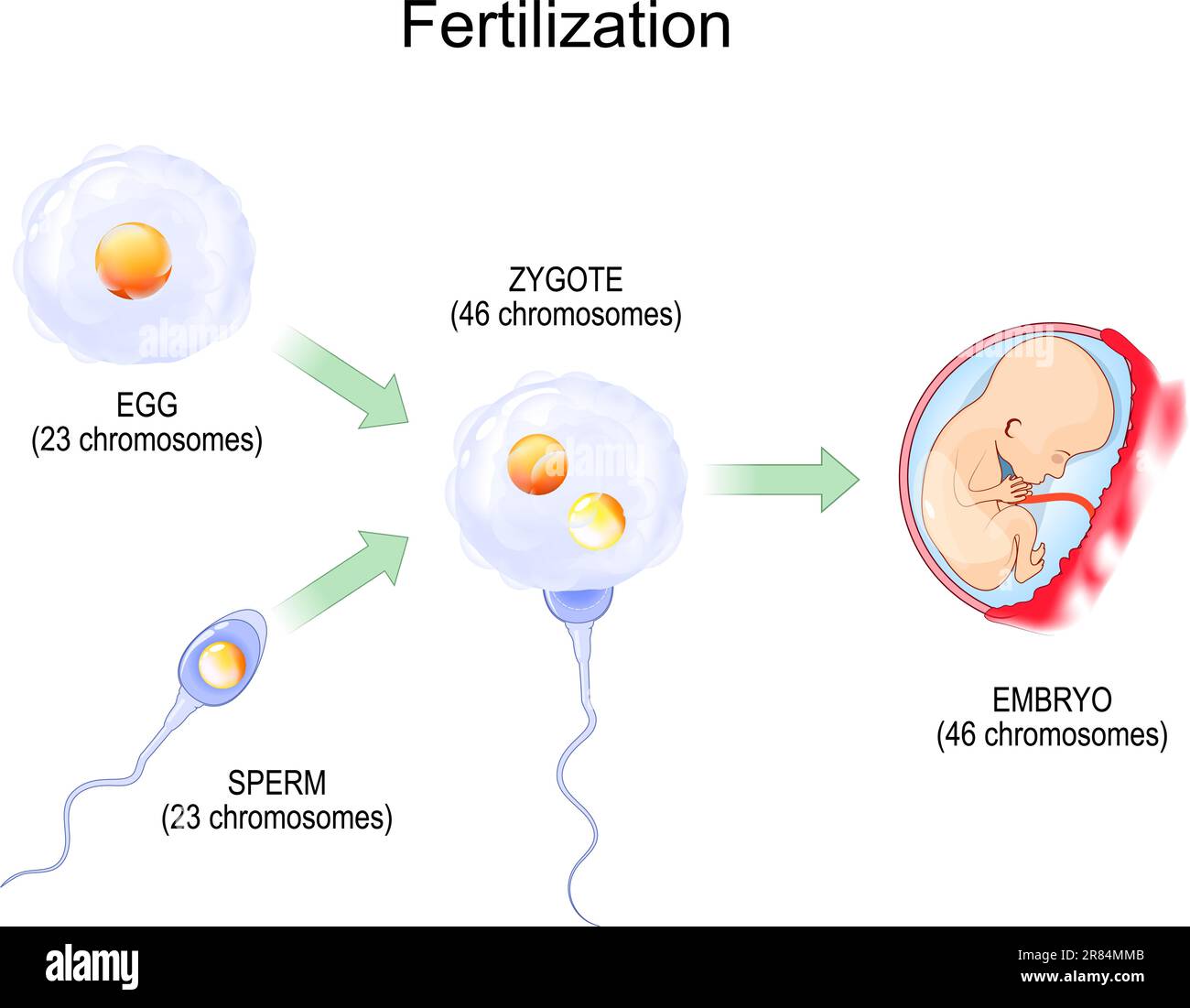
The Diploid Life Cycle. Organisms that reproduce sexually (like humans) have a diploid-dominant life cycle and spend most of their lives as diploid adults. Two haploid gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote Diploid Cells vs. Haploid Cells. The key differences between haploid and diploid cells are summarized in the table below. Diploid Cells Haploid vs. diploid refers to the number of chromosomes and chromosome sets present in the cell. How Does DNA Work? Unusual words like "ploidy" are a good starting point when diving into the study of a cell's DNA and life cycle. Ploidy refers to the number of chromosomes present in the cell. Simple organisms like bacteria only have a Plants exhibit haplodiplontic life cycle wherein the gametes (sex cells) are not a direct product of meiosis. Instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. Throughout the plant life cycle, all plants undergo the alternation of generations. This cycle of generations include both diploid (2n) phase, the sporophyte, and the haploid (n) phase gametophyte.
Life Cycles of Sexually Reproducing Organisms Biology Diagrams
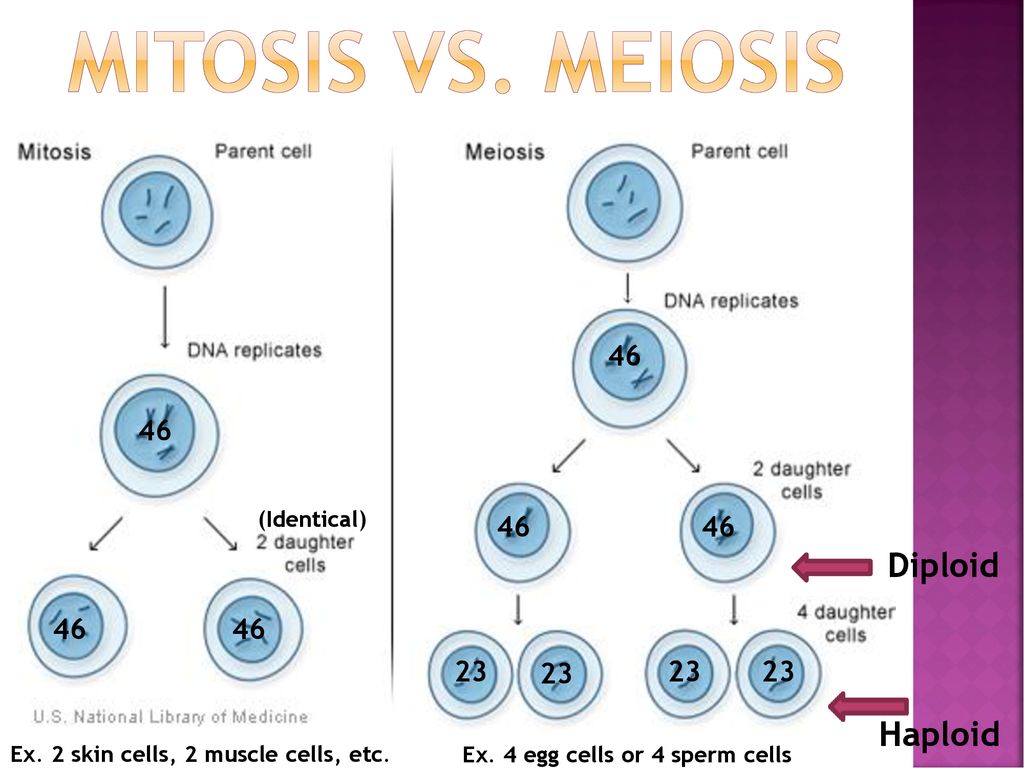
The cell cycle of diploid eukaryotic cells is divided into two main phases: Interphase: where the cell prepares for cell division; Mitosis: the actual cell division itself; This is the same for haploid cells responsible for sexual reproduction, except the type of cell division is known as meiosis.This is the process of cell division where one diploid cell separates and gives rise to four
