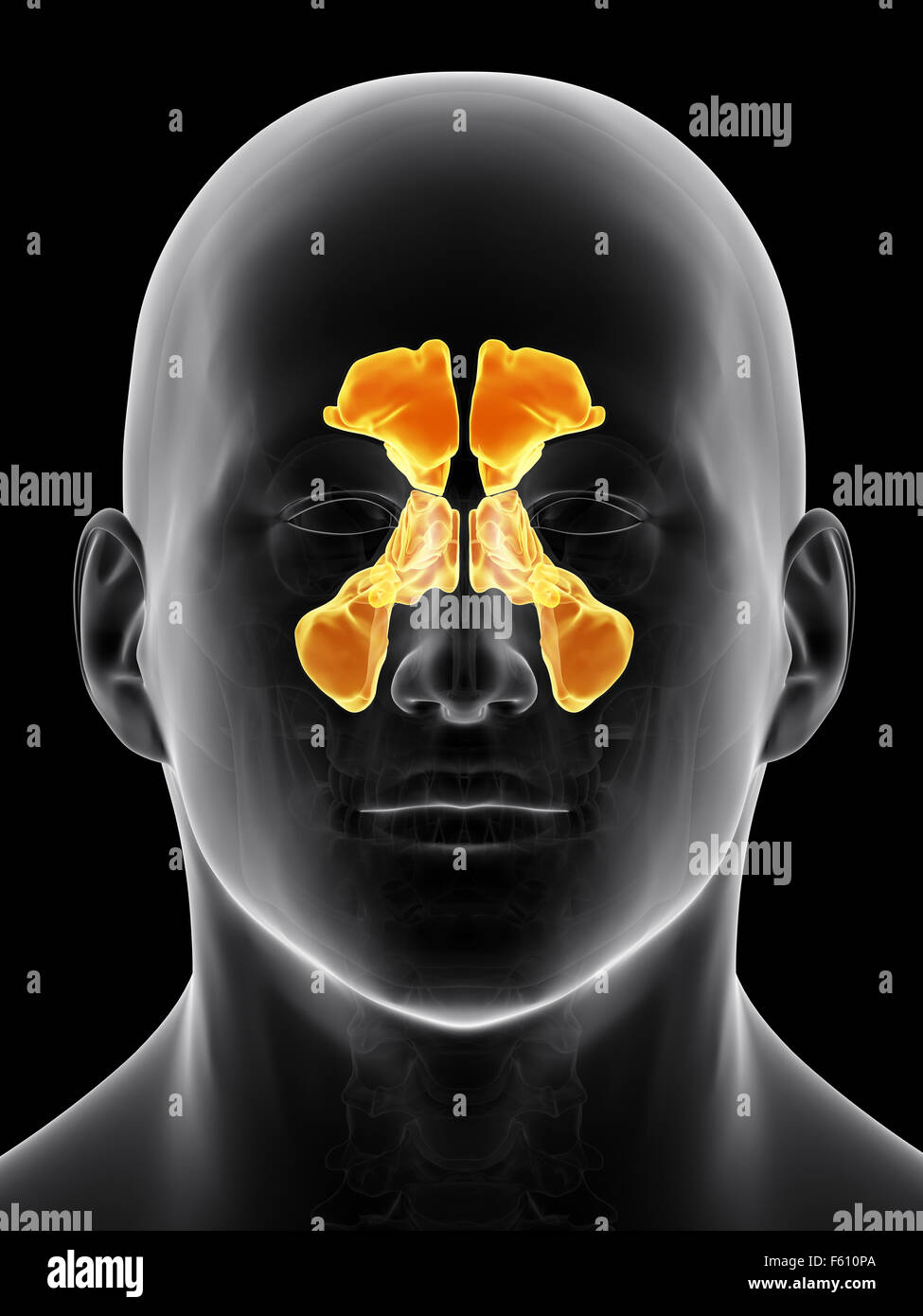
Head Anatomy Stock Illustration Biology Diagrams The paranasal sinuses (the hollow spaces in the skull and facial bones around the nose) are air-filled cavities within the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary bones.[1] They are outgrowths from the nasal cavity. All of them drain into the superior or lateral aspect of the nose.[2] The sinuses' lining mucosa is continuous with the nasal cavity; therefore, any infections from the nasal Anatomy of the Sinuses Sinus Center The internal maxillary artery arises from the external carotid artery and divides into several branches in the head and neck before entering the nasal cavity. The largest branch is the sphenopalatine artery that enters the nasal cavity through a tunnel located along the lateral nasal wall near the back of Understanding the Paranasal Sinuses. The paranasal sinuses, often referred to as "the sinuses," are hollow spaces found within the facial bone called the frontal bone. Each sinus is named after the bone it's located in. Here's a brief look at each: Maxillary Sinuses: These are found on each side of the face within the cheekbone.
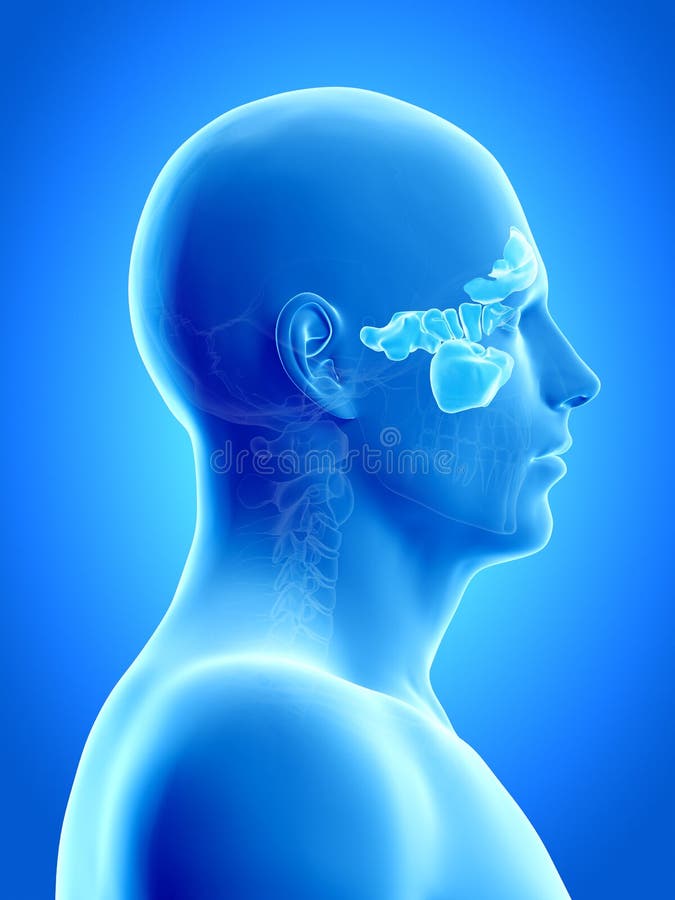
Sinus (anatomy) 15 languages. The pressure is often experienced in the cheek area, eyes, nose, on one side of the head (temple areas), and can result in a severe headache. [2] When diagnosing a sinus infection, one can identify which sinus cavity the infection is located in by the term given to the cavity. Ethmoiditis refers to an infection The sigmoid sinus is a dural venous sinus that lies deep within the human head, and just below the brain. A dural sinus is a channel that lies between… READ MORE Learn about sinus anatomy here. Sinus Anatomy: Check Out This Helpful Diagram - NY Sinus Center and can even spread as far as the occipital bone near the back of the head if they are very large. Although the sinuses can become inflamed and cause a great deal of pain, they are vital to keeping our lungs free of debris.

Anatomy, Head and Neck, Sinus Function and Development Biology Diagrams
Unlike your other sinuses, each ethmoid sinus cavity consists of many tiny cavities (or pockets) called air cells. Your ethmoid sinuses hold between 2 to 3 mL of air. Maxillary sinus: Your maxillary sinuses are in your maxillary bone, the bone that makes up your upper jaw. They're symmetrical, pyramid-like cavities, located beneath your eyes Discover the four sinuses in your head, how they function, and what symptoms are associated with sinusitis. Visit CT Sinus Center for expert sinus care. Waterbury (203) 574-5997 The American Rhinologic Society breaks down the paranasal anatomy with corresponding images on their website. Maxillary sinus: one sinus located within the bone of Finally, the sphenoidal sinuses are in the body of the sphenoid. They open into the posterior wall of the sphenoid-ethmoidal recess. Dural Venous Sinuses. The dural venous sinuses are in the brain. The venous drainage of the brain begins as networks of small canals that drain into the larger vein, which then empty into the dural venous sinuses.