How to Read a Food Web Biology Diagrams The Cheetah: A Remarkable Carnivore. Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) are fascinating members of the big cat family, primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, with a small population in Iran.They stand out not just for their speed—capable of reaching up to 70 miles per hour—but also for their unique adaptations that class them distinctly in the animal kingdom.

Lastly, top predators, eat the secondary consumers and regulate the entire food chain. Cheetah Food Chains. Cheetahs are a top predator in the African Savanna. They are large, tan cats with black Food chains of the savanna. This section is going to be about a three food chains of the savanna Secondary Consumer: The secondary consumers in these food chains are the cheetah, hyena, and the lion. Tertiary Consumer: Teritary consumer in these food chains is the vulture.

African Grassland (Savanna) Food Web Biology Diagrams
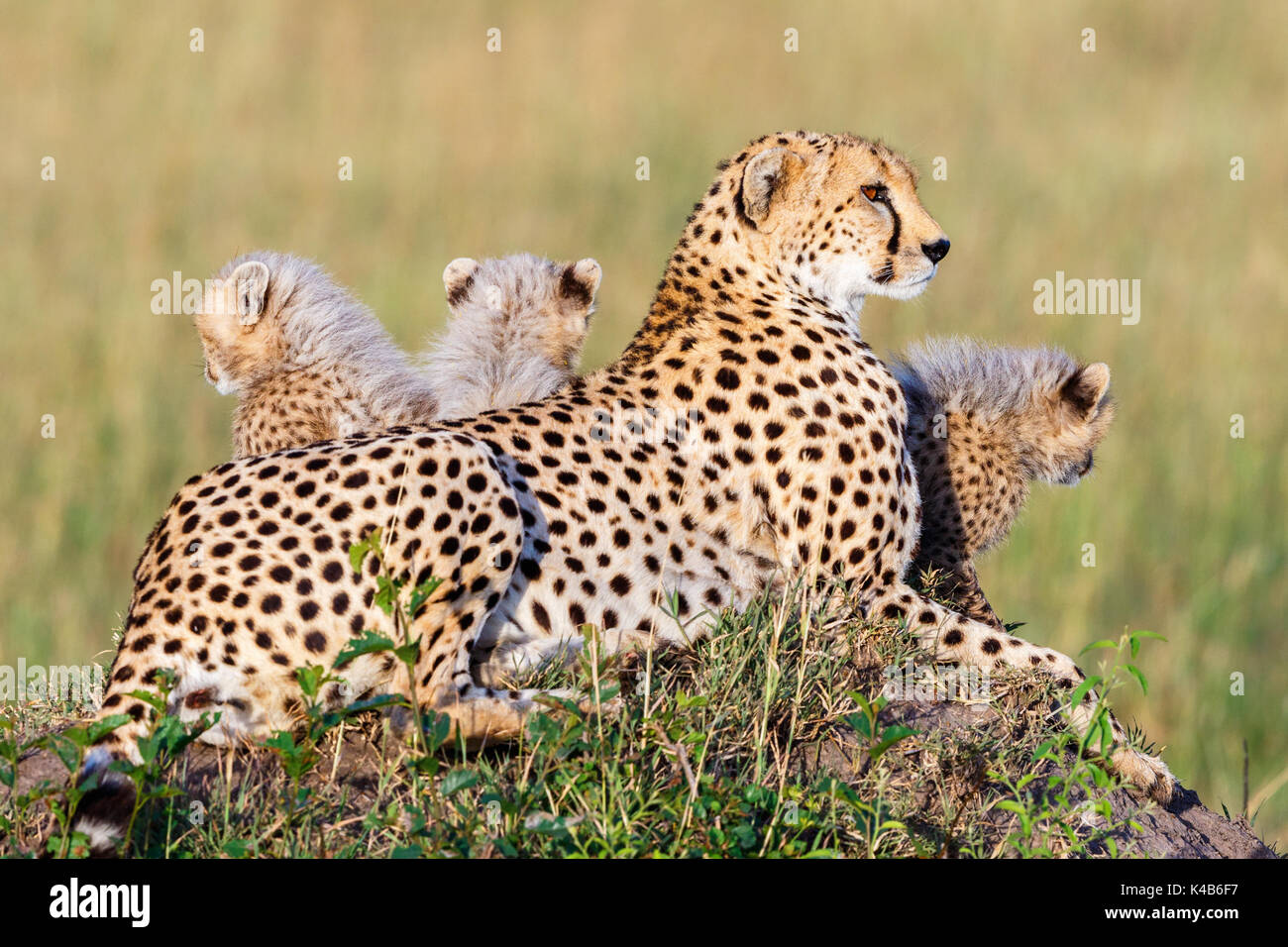
A simplified illustration of the food web of a savanna ecosystem. Every animal species has its role (or niche) in the ecosystem that it lives in. As a carnivorous predator, the cheetah's role in the ecosystem is important as it helps to maintain balanced and healthy food webs.

Cheetah | Image Source: Natural Habitat Adventures. ⫸ Conclusion. The savanna food web is a marvel of interconnectedness. Every organism plays a crucial role, from the grasses that fuel the grazers to the predators that maintain populations. This delicate balance is vulnerable - changes at one level ripple throughout the system. As you move up the food chain, each level receives only about 10% of the energy from the level below it. This energy loss limits most food chains to 3-4 trophic levels. Savanna food chains follow these same principles as energy transfers between trophic levels, beginning with producers. Savanna Food Chain Trophic Levels and Components Explained

Food Chain Biology Diagrams
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem. It illustrates the complex relationships among all organisms in an ecosystem, demonstrating that animals rarely consume just one thing. 10. What are the typical food chains in the savanna where cheetahs live? Savanna food chains often begin with producers such as grasses
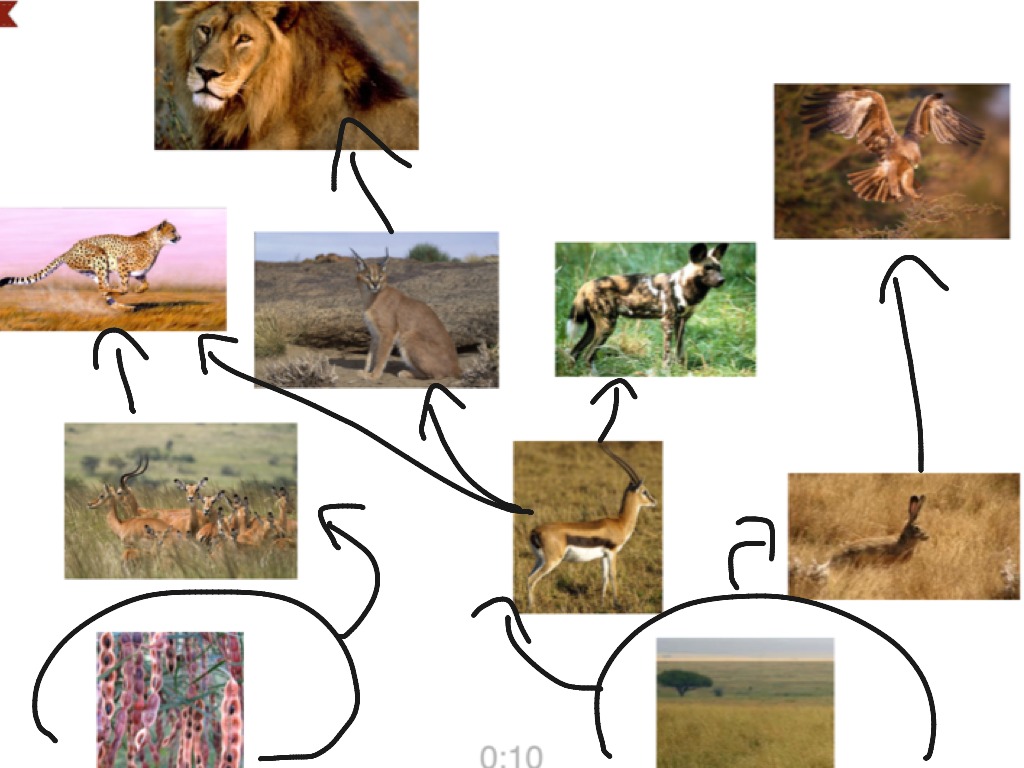
The food chain throughout the African savanna is shown on the left here. Plants and trees are the producers who photosynthesize, creating macromolecules which primary consumers such as zebras, steenbok, or elephants use to gain energy. These are primary consumers are then in turn eaten by secondary consumers such as cheetahs, hyenas or lions. This is an African Savanna Food Web.See if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. Look for: The Producers - the trees, shrubs and grass.. The Primary Consumers - the zebras and elephants.. The Secondary Consumers - the cheetah, hyena.. The Scavengers - the termites, vultures and hyena.. The Decomposers or Detritivores - mushrooms
