Nucleolar Separation from Chromosomes during Aspergillus nidulans Biology Diagrams These nucleolar functions are realized predominantly in interphase and, apparently, are abolished during mitosis, when the nucleolus disassembles. In this review, literature and our own data on the dynamics and mechanisms of the nucleolus disassembly and reassembly during mitosis in animal and plant cells are summarized.

The dynamics of the processing nucleolar proteins was analyzed at the transition mitosis/interphase. Rapid time-lapse videomicroscopy was used to follow GFP-tagged processing proteins in the volume of the cells from metaphase to G1 (Fig. 5 ). Nucleolar dynamics throughout mitosis. Using different cell biology and biochemistry techniques 28,60,61,62 it has been documented that the nucleolar structure and biomolecular dynamics change

The dynamics of the nucleolus Biology Diagrams
The dynamics of nucleolus during mitosis. The nucleolar disassembly and reassembly pathway are shown in a-c and d-i, respectively. During disassembly, (a and b) the RPA39 (blue) dissociates from the nucleoli ∼2 min before the loss of functional integrity of the NE as illustrated by the leakage of IBB (gray).

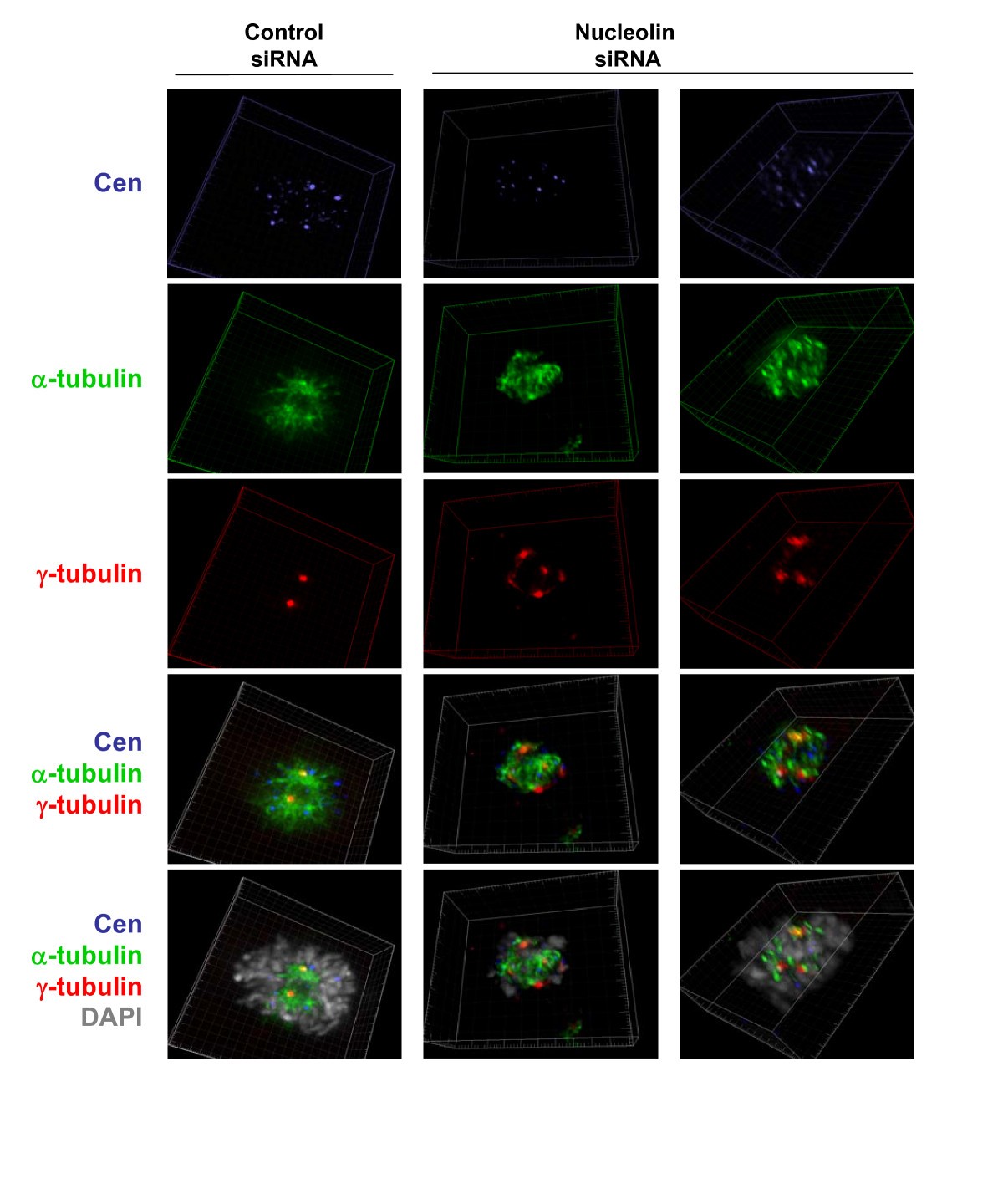
The current view of nucleolar reformation at the end of mitosis is that the process begins in late anaphase or early telophase when RNA pol I transcription is reinitiated (Scheer et al. 1993; Dynamics of nucleolar reassembly in telophase. CMT3 cells in telophase, which were transiently expressing the fibrillarin-GFP protein, were subjected Entry into mitosis correlates with nucleolar disassembly and shutdown of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene (rDNA) transcription. In telophase, nucleoli reform and transcription is reactivated. The molecular mechanisms underlying the dynamics of nucleolar transcription during the cell cycle are manifold. After mitosis, human nuclei initially contain 10 nucleoli, which later fuse to form fewer larger ones (Savino et al., 2001). Thus, due to the changing nucleolar number, the likelihood of their coalescence is expected to vary with the cell cycle progression. Thank you for submitting your article "Nucleolar dynamics and interactions with
The nucleolus as a multiphase liquid condensate Biology Diagrams
Schematic illustration of nucleolar disassembly at the beginning of mitosis. In the G 2 phase of the cell cycle, the nucleolus is composed of 3 structures corresponding to different steps of ribosome biogenesis: (1) the fibrillar center or FC (white octagon) were the ribosomal genes (rDNAs) are localized, (2) the dense fibrillar component or DFC (D in green) corresponding to transcription of In the vast majority of eukaryotic somatic cells the nucleolus is the largest and the most dynamic nuclear domain. The canonical nucleolar function is ribosome biogenesis, which includes ribosomal DNA (rDNA) transcription, pre-rRNA processing and ribosomal subunit assembly. Furthermore, according to recent data the nucleolus and specific nucleolar proteins participate in cell cycle regulation
