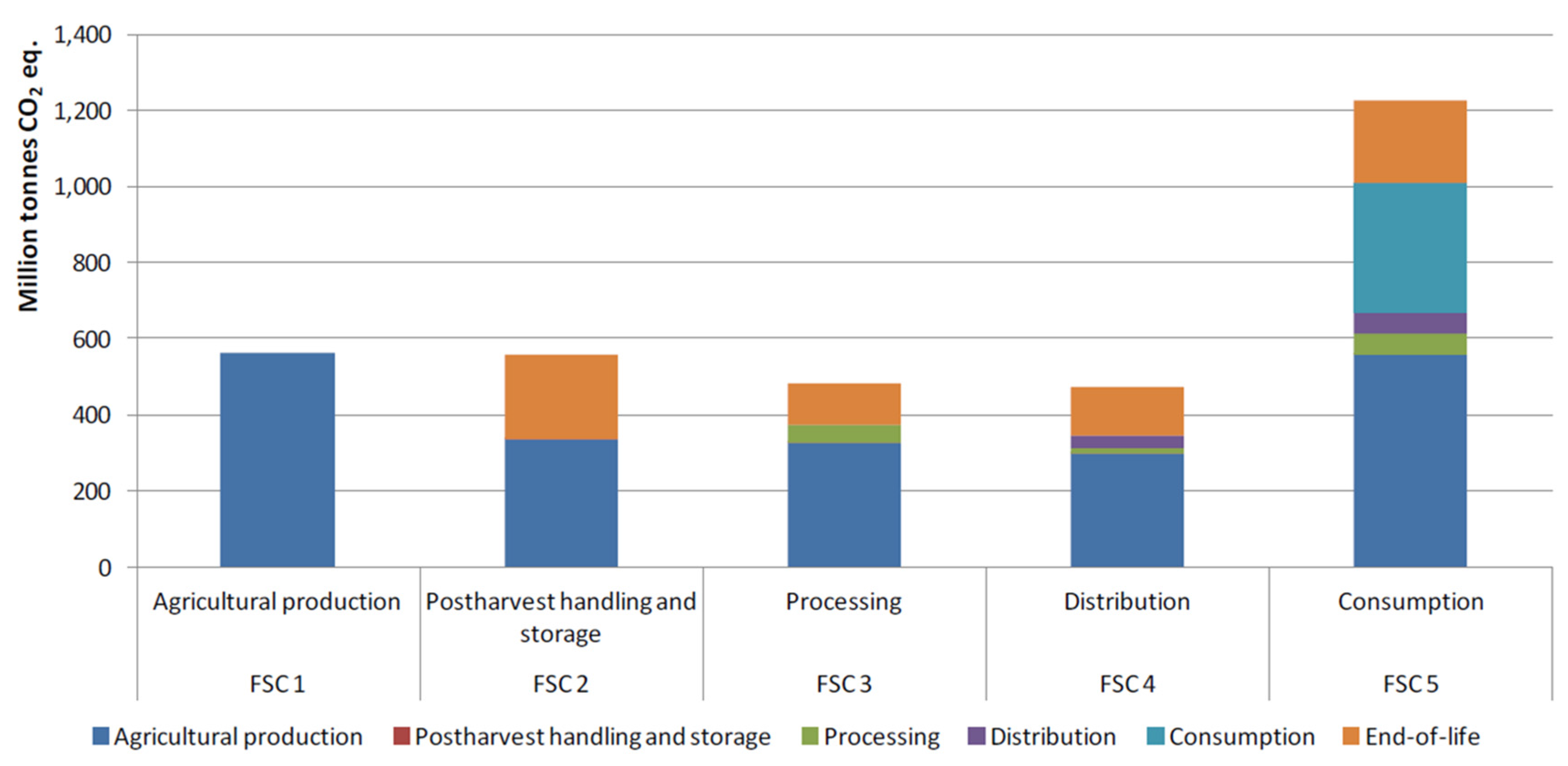
Royal Society Open Science Biology Diagrams Maria Masoura outlines the drivers of supply chain disruption and their ripple effects on global food security.. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines food security as when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life. In recent years, our food supply chain facing various disruptions shows a need for higher resilience and sustainability. To better prepare for future uncertainties the food supply chain may encounter, it is imperative to understand the status quo of the food supply chain resilience literature, which focuses on deploying digital technology and integrating sustainability in supply chain management. In this context, food supply chain disruptions can refer to any significant failure in the flow of food products from production to consumption [78], representing highly complex risks that can affect the operation and infrastructure of food systems.Supply chain disruption and uncertainty risks are growing, and modern Food Supply Chains (FSC) are among the most vulnerable to such threats [11].

The predicted alterations in global climate provide opportunities and challenges for society and the economy. Designing effective strategies to solve climate change issues represents a vast opportunity (Allison et al., 2009).A better comprehension of the climate change-related elements influencing the food supply chain's susceptibility is vital to lower the risks of food and nutrition Understanding how disruption in the food chain affects the ecosystem is crucial for addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainability. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of the food chain, explore the causes of disruptions, and analyze their far-reaching impacts. The food supply chain (FSC) is a complex and dynamic system that faces both challenges and opportunities in the era of globalization. It operates with an intense network of interrelated processes involving cultivation, processing, distribution, and consumption, ranging from production to consumption. However, this intricate network is susceptible to disruptions caused by transportation delays

Food supply chain disruptions and its resilience: a framework and ... Biology Diagrams
1. Introduction. Food is a basic need for humans but the way in which much of it is produced, distributed, and consumed, is not sustainable. Challenges include among other things, biodiversity loss, climate change, environmental degradation, diet-related diseases, and unequal access to food (Schneider et al., Citation 2023).A 'food system' perspective helps to better understand the root
The absence of animals would not simply mean a quieter world; it would unravel the intricate web of life, leading to ecosystem collapse, food chain disruptions, and severe impacts on human well-being and survival. The Devastating Domino Effect. The immediate impact of animal disappearance would be a massive disruption of food chains and