Stem Cell Mechanobiology and the Role of Biomaterials in Biology Diagrams Stem cells transplant and tissue regeneration methods for treating various diseases have rapidly grown in usage over the past decades or so. There are different types of stem cells such as mesenchymal, hematopoietic, embryonic, mammary, intestinal, endothelial, neural, olfactory, neural crest, testicular and induced pluripotent stem cells.
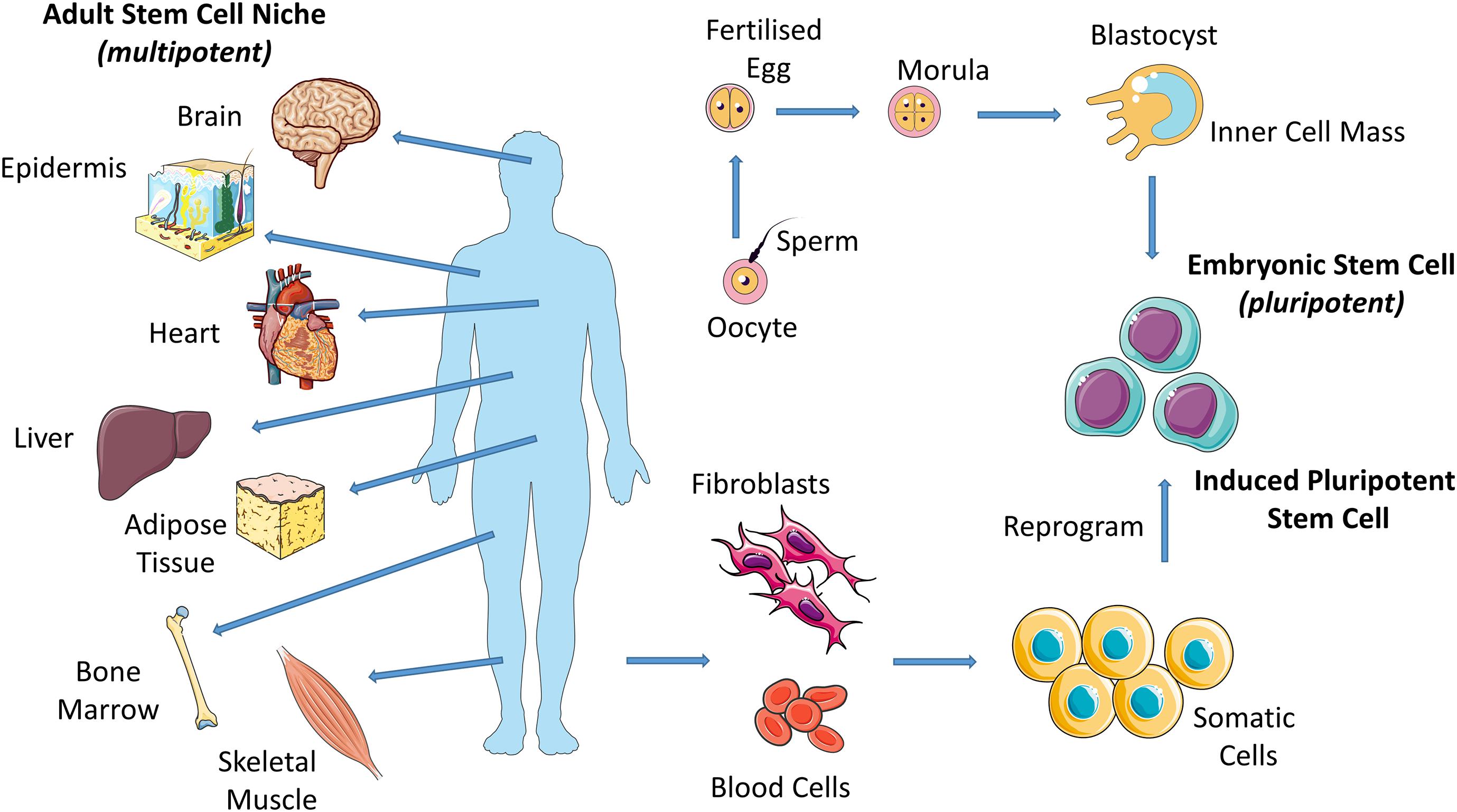
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives. It is the next chapter in organ transplantation and uses cells instead of donor organs, which are limited in supply.
Tissue Stem Cells: Architects of Their Niches Biology Diagrams
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cell, micrografts, tissue regeneration, autologous, wound management, ulcer. Introduction. The correct histological structure of a given tissue plays a pivotal role in allowing appropriate function and optimizing the activities to which that tissue is predisposed. Unfortunately, many factors can alter the physiology In contrast to epidermal stem cells, which continually regenerate tissue, hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs) alternate between extended bouts of quiescence and active tissue regeneration (Figure 1B). In mice, much of the regeneration energy in the absence of injury is devoted to synchronous cycles of hair coat production, which is fueled by stem Regenerative engineering is a rapidly growing field that harnesses advancements made in the field of tissue engineering with stem cell biology, materials science, and developmental biology. There has been successful production of clinically relevant therapies and technologies that improve patient outcomes and will continue to do so.
Regenerative medicine aims at repairing, replacing or regenerating cells, tissues and organs to restore impaired function 9.New insights in developmental biology, stem cell biology and In some cases, stem cells do not appear to be taking center stage in the repair and regeneration of tissue but are key players nonetheless. In the kidney, it was found that when the tubules used for drawing off waste fluids from the blood are damaged, it is the mature epithelial cells, not stem cells, which step in to rebuild the tissue. The field of tissue repair and wound healing has blossomed in the last 30 years. We have gone from recombinant growth factors, to living tissue engineering constructs, to stem cells. The task now is to pursue true regeneration, thus achieving full
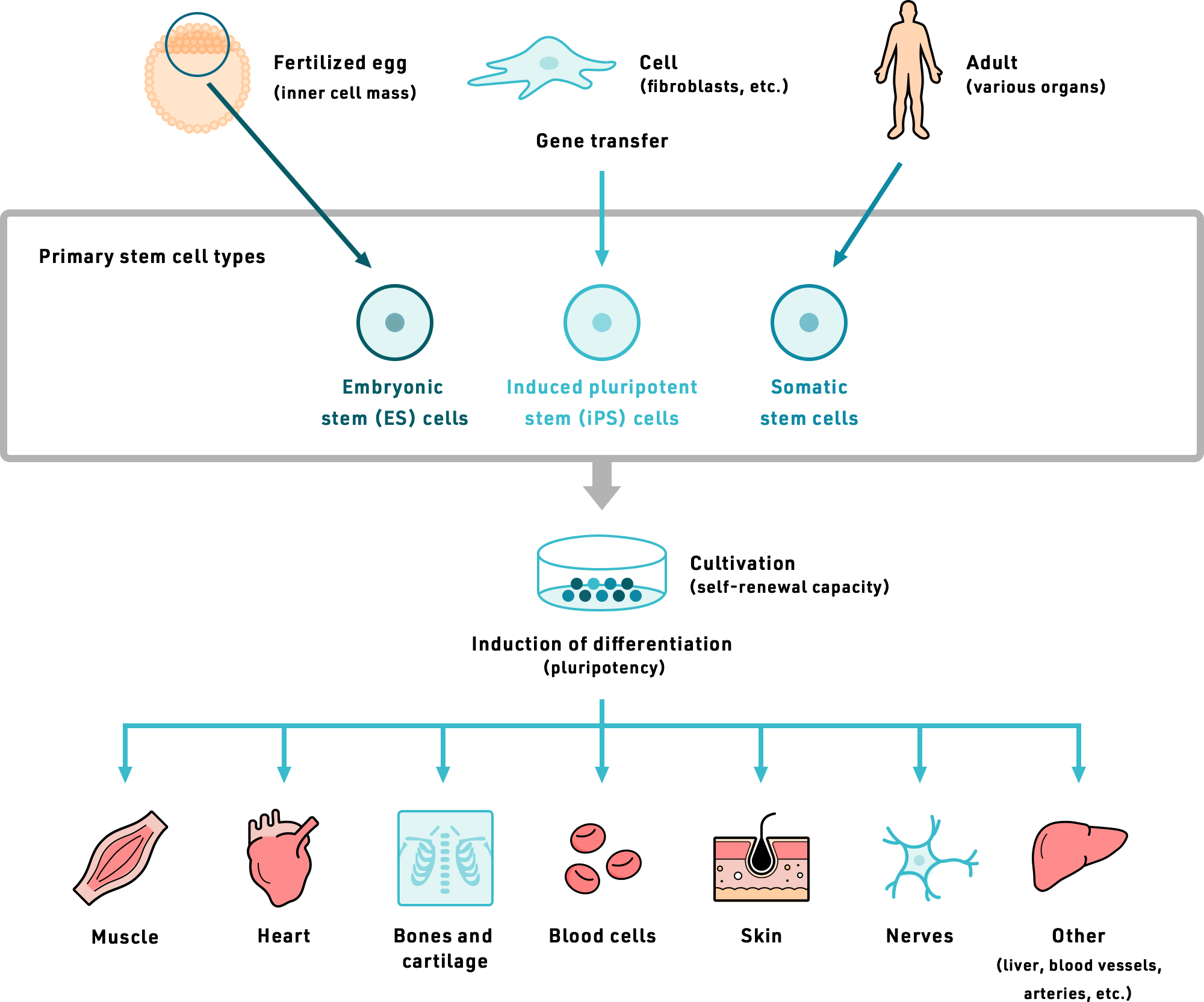
Tissue regeneration: an overview from stem cells to micrografts Biology Diagrams
The regeneration of injured tissues by exogenous and endogenous stem cells relies on the local microenvironment being conducive to repair. Chronic diseases confer tissue and organ damage that Many tissues regenerate without using stem cells by duplicating parenchymal cells, and dedifferentiation is a process that can assist in this. In innate regenerative biology, dedifferentiation typically refers to the tempering of functional properties of a specialized adult cell. This process can involve the reduced expression of signature
