The Cell Cycle Notes Also a unicellular Biology Diagrams Concept 12.3 The cell cycle is regulated by a molecular control system. The Lives of a Cell - Notes of a Biology Watcher. This Is Biology - The Science of the Living World. The Diversity of Life. ch_11_ilban_cell_communication.pdf. ch_10_ilban_photosynthesis.pdf AP Biology Forums. Three Things to Know about the Cell Cycle: Interphase consists of three stages: G1 (first gap phase), S (synthesis, in which DNA replication occurs), and G2 (second gap phase). Interphase is followed in somatic cells by mitosis. Mitosis is the process in which a cell produces two identical daughter cells. • The cell cycle appears to be driven by specific chemical signals in the cytoplasm. • Fusion of an S phase cell and a G 1 phase cell induces the G 1 nucleus to start S phase. • Fusion of a cell in mitosis with one in interphase induces the second cell to enter mitosis. • The distinct events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct

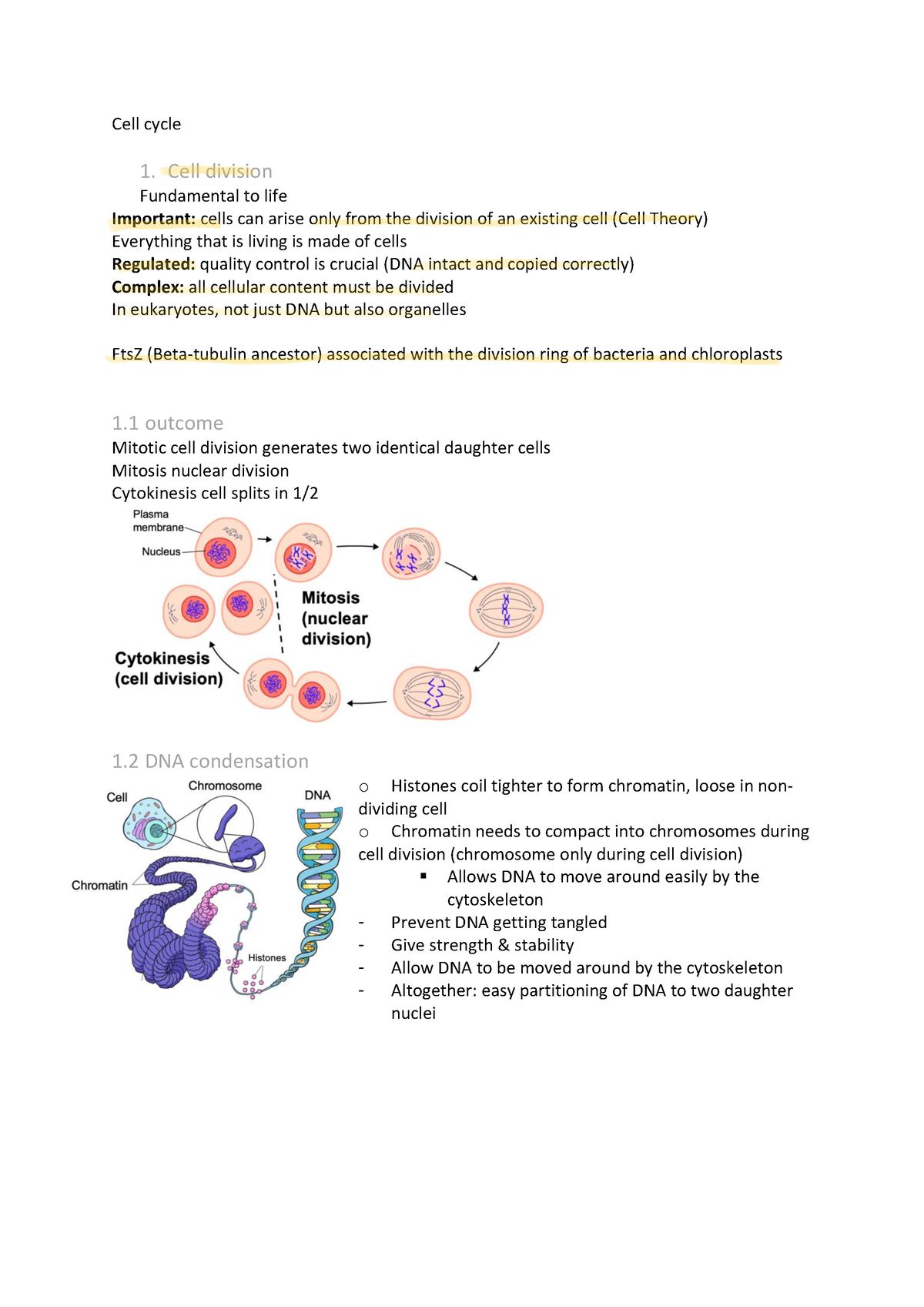
The cell cycle is the highly regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next The cell cycle has three phases: interphase : during interphase the cell grows and carries out its normal cellular functions, e.g. synthesizing proteins and replicating DNA ready for mitosis

CliffsNotes Biology Diagrams
During interphase, the cell spends most of its time performing the functions that make it unique. Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle during which the cell divides into two daughter cells. Interphase. The interphase stage of the cell cycle includes three distinctive parts: the G 1 phase, the S phase, and the G 2 phase. The G 1 phase follows

The period required to complete one cell cycle (from beginning of one cell division to the beginning of next) is called generation time. It is 24 hours in human cells and 90 minutes in yeast. Cell cycle is simpler in prokaryotes and more complex in eukaryotes.
PDF Notes Biology Diagrams
Following interphase, the cell enters the M phase, which consists of mitosis and cytokinesis.Mitosis is the process where replicated chromosomes are evenly distributed into two new nuclei, while cytokinesis involves the physical separation of the cytoplasm and organelles, culminating in the formation of two distinct daughter cells. This orderly progression through the cell cycle is
